Stars
Astronomical objects that paint the sky every night

A star is a very large ball of bright glowing hot matter in space. That matter is called plasma. Stars are held together by gravity. They give out heat and light because they are very hot.
The Sun is a star at the centre of the solar system.
The amount of material in a star (its mass) is so huge that it starts a nuclear reaction going. The reaction changes hydrogen to helium and gives off heat.
Stars like the Sun are hot because this nuclear reaction happens inside them. The reaction is called nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion makes light and heat and makes bigger chemical elements. In the Sun (but not all stars) the change which takes place is the production of helium, with minute (very small) amounts of heavier elements.
Stars have a lot of hydrogen. Nuclear fusion changes hydrogen into helium. Fusion makes a lot of energy. The energy makes the star very hot. The energy produced by stars moves (radiates) away from them. Much of the energy leaves as light. The rest leaves as other kinds of electromagnetic radiation.
When a star like the Sun gets old, it will expand in size and become a red giant star. That will happen in about a billion years' time (109 years).
Latest updates!
All the news in one place.
Earth Sun
The star nearest to Earth is the Sun. The energy from the Sun supports almost all life on Earth by providing light for plants. Plants turn the light into energy in a process called photosynthesis. The energy from the Sun also causes weather and humidity on Earth.
We can see other stars in the night sky when the Sun goes down. Like the Sun, they are made mostly of hydrogen and a little bit of helium plus other elements. Astronomers often compare those other stars to the Sun. For example, their mass is given in solar masses. A small star may be 0.2 solar masses, a big one 4.0 solar masses.
The Earth and other planets move around (orbit) the Sun. The Sun and all things that orbit the Sun are called the Solar System. Many other stars have planets orbiting them: those planets are called exoplanets. If you were on an exoplanet, our Sun would look like a star in the sky, but you could not see the Earth because it would be too far away.
The life of stars
Stars are made in nebulae. These are areas that have more gas than normal space. The gas in a nebula is pulled together by gravity. The Orion nebula is an example of a place where gas is coming together to form stars.
Stars spend most of their lives combining (fusing) hydrogen with hydrogen to make energy. When hydrogen is fused it makes helium and it makes a lot of energy. To fuse hydrogen into helium it must be very hot and the pressure must be very high. Fusion happens at the center of stars, called "the core".
The smallest stars (red dwarfs) fuse their hydrogen slowly and live for 100 billion years. Red dwarfs live longer than any other type of star. At the end of their lives, they become dimmer and dimmer. Red dwarfs do not explode.
When very heavy stars die, they explode. This explosion is called a supernova. When a supernova happens in a nebula, the explosion pushes the gas in the nebula together. This makes the gas in the nebula very dense (thick) . Gravity and exploding stars both help to bring the gas together to make new stars in nebulas.

Most stars use up the hydrogen at their core. When they do, their core becomes smaller and becomes hotter. It becomes so hot it pushes away the outer part of the star. The outer part expands and it makes a red giant star. Astro-physicists think that in about 5 billion years, the Sun will be a red giant. Our Sun will be so large it will eat the Earth. After our Sun stops using hydrogen to make energy, it will use helium in its very hot core. It will be hotter than when it was fusing hydrogen. Heavy stars will also make elements heavier than helium. As a star makes heavier and heavier elements, it makes less and less energy. Iron is a heavy element made in heavy stars.
Our star is an average star. Average stars will push away their outer gases. The gas it pushes away makes a cloud called a planetary nebula. The core part of the star will remain. It will be a ball as big as the Earth and called a white dwarf. It will fade into a black dwarf over a very long time.
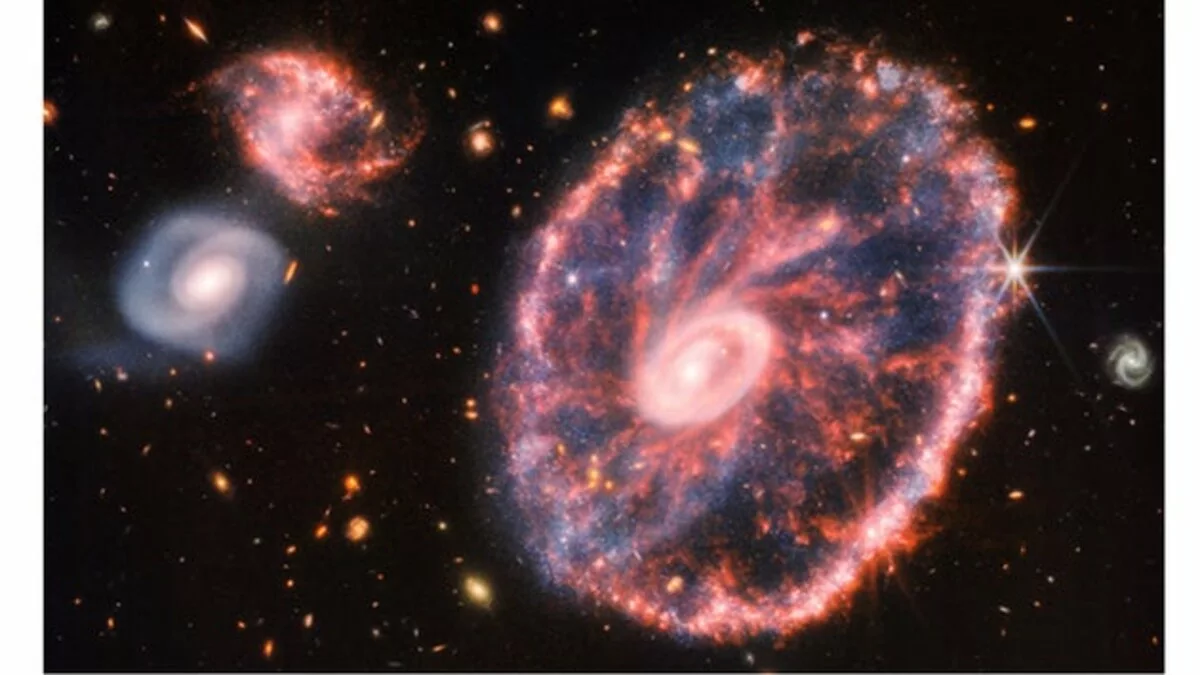
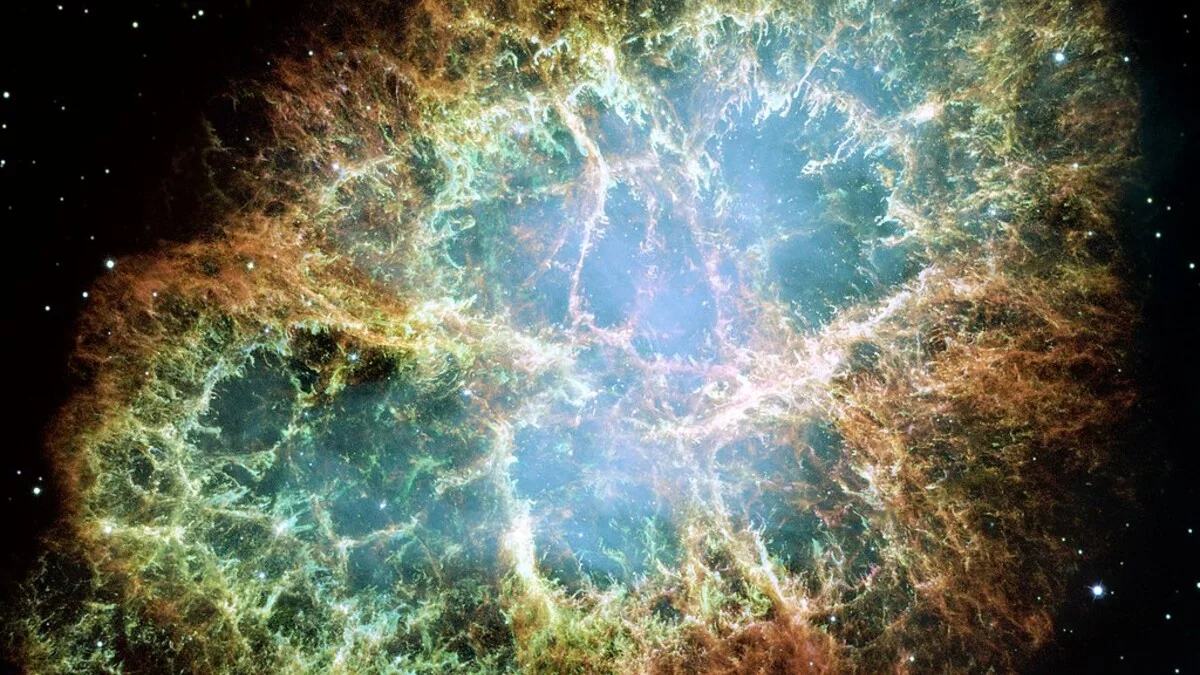





Later in large stars, heavier elements are made by fusion. Finally the star makes a supernova explosion. Most things happen in the universe so slowly we do not notice. But supernova explosions happen in only 100 seconds. When a supernova explodes its flash is as bright as a 100 billion stars. The dying star is so bright it can be seen during the day. Supernova means "new star" because people used to think it was the beginning of a new star. Today we know that a supernova is the death of an old star. The gas of the star is pushed away by the explosion. It forms a giant cloud of gas called a planetary nebula. The crab nebula is a good example. All that remains is a neutron star. If the star was very heavy, the star will make a black hole. Gravity in a black hole is extremely strong. It is so strong that even light cannot escape from a black hole.
The heaviest elements are made in the explosion of a supernova. After billions of years of floating in space, the gas and dust come together to make new stars and new planets. Much of the gas and dust in space comes from supernovae. Our Sun, the Earth, and all living things are made from star dust.

